Gonorrhoea Cases Rise In Melbourne, Suburbs

A Gonorrhoea outbreak in Melbourne and its suburbs has led to concerns among public health experts, with cases of the sexually transmitted infection rising in the past decade.
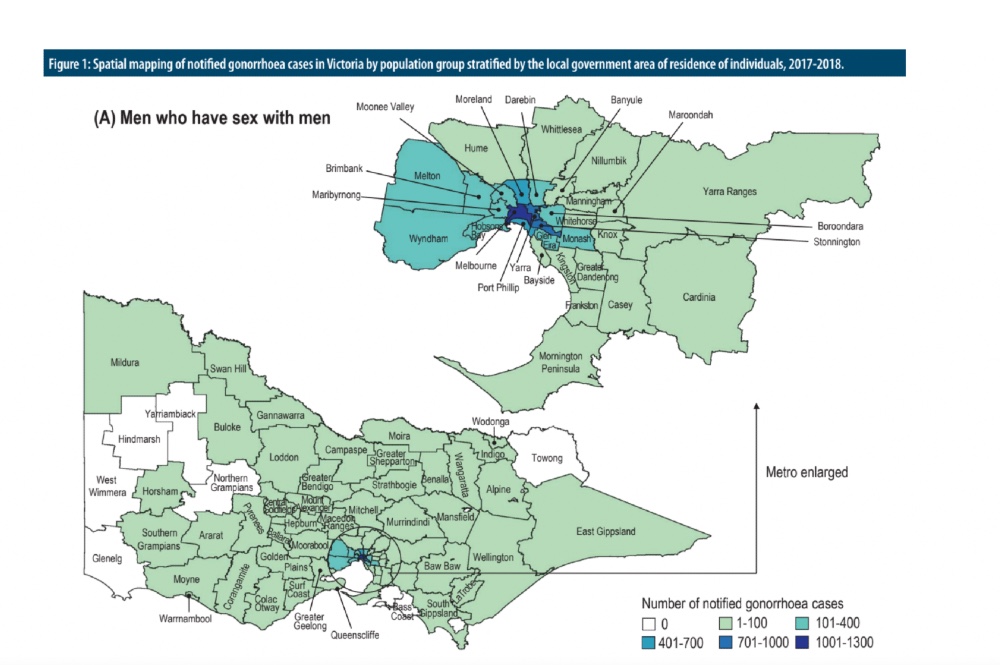
A new study from Alfred Health has for the first time geographically mapped the distribution of gonorrhoea infections in the 79 local government areas in Victoria.
The study found that between 2017 and 2019, around 24,825 cases of gonorrhoea were notified in Victoria. Around 43 % of the infections were among gay men (41% or 10,386 cases) and bisexual men (one per cent or 279 cases).
Cases Among Gay Men In Inner Suburbs
Assistant Prof Eric Chow, Sexual Health Epidemiologist, who led the study said that “gay, bisexual and other men who have sex with men have been disproportionately affected by gonorrhoea.”
Cases among gay men were concentrated in Melbourne and the inner suburbs like Yarra and Stonnington.
Since 2010, there has also been a steady rise in gonorrhoea infections among heterosexual men and among women – the reasons behind the increase in infections, Chow said, was “not well understood”.
Around 20 % of the gonorrhoea infections between 2017 and 2019 were among women, 13 % among heterosexual men and 24 % among those who had not mentioned their gender or listed it as ‘other’.
Gonorrhoea cases in women were concentrated in inner Melbourne and suburbs like Melton and Case, while among heterosexual men, in addition to inner Melbourne, many of the cases were in the suburbs of Casey and Brimbank.
Pattern Similar To Syphilis Outbreak In Melbourne
The geographical mapping of cases shows that the infections show a similar pattern to the outbreak of syphilis infections, which have seen an increase in the past decade as well.
“This demonstrates that no matter who you are or where you live, looking after your sexual health is important for us all,” Thorne Harbour’s Director of Health Promotion, Policy, and Communications, Colin Batrouney told Star Observer.
“This includes regular sexual health screening. By getting tested for Gonorrhoea, Syphilis and other STIs we can look after our health as well as that of our sexual partners,” added Batrouney.
What Is Gonorrhoea?
Gonorrhoea, also known sometimes as “clap” is a sexually transmitted bacterial infection caused by the bacterium Neisseria gonorrhea. It can affect the penis, anus, throat, eyes and vagina and can be spread by unprotected oral, anal or vaginal intercourse with a person who has gonorrhea. It can also be passed by fingering, fisting or using toys and by fingers or hands from the genitals to the eyes.
According to THH’s Drama Down Under campaign, “the most effective way to help prevent gonorrhoea is to use condoms, dams and gloves during sex”. Regular sexual health tests can help prevent it from spreading.
The infection can be easily treated with a short course of antibiotics. If left untreated, it can can “cause permanent damage to the eyes, joints, heart or brain”.
For more information on where to get tested for gonorrhoea and other sexually transmitted infections, check Thorne Harbour Health’s The Drama Down Under website.